Not all Uranium ETFs are the same
As interest in nuclear energy comes to the fore, understanding the different options on ASX is paramount.
Nuclear energy is gaining momentum as a clean, reliable solution powered by innovation across mining, technology, and utilities.
- Nuclear energy offers stable, carbon-free power critical for global electrification and AI-driven demand.
- Innovation across mining, reactors, and utilities is reshaping the nuclear energy value chain.
- Support among global governments and new technologies is creating long-term opportunities in the nuclear sector.
As demand for clean, reliable energy surges, nuclear power is emerging as a critical player in the global shift away from fossil fuels. With the ability to generate massive amounts of electricity without large amounts of emissions, nuclear energy is being considered as a solution to the world's energy needs. Nuclear power provides a steady, around-the-clock energy supply that is ideal for supporting the increasingly power-hungry infrastructure of modern society and new technologies such as artificial intelligence.
Nuclear energy has evolved from the reactors we’ve seen in the past; today’s leading companies are reimagining the potential of nuclear power with new technologies like small modular reactors (SMRs), advances in nuclear fuels, and portable microreactors. These innovations aim to make nuclear safer, more efficient, and accessible for a wider range of applications, from powering cities to remote industrial sites.
The top uranium and energy innovators leading the industry
Uranium and the companies mining the element often come to mind first when considering nuclear energy, especially for Australian investors, because of our rich deposits. Uranium is the essential fuel that powers nuclear reactors, and these miners sit at the very beginning of the nuclear supply chain.
However, the nuclear industry extends well beyond uranium miners. Some of the most groundbreaking innovations are happening further down the line in the Industrials and Utilities segments. Industrial companies are leading the charge in developing next-generation reactors, modular technologies, and advanced safety solutions that make nuclear power more efficient and versatile than ever. Meanwhile, utilities play a key role in generating and distributing nuclear power to cities and industries, supporting everything from household electricity to the ever-growing needs of data centers and AI.
Recently we highlighted four key catalysts that have been driving investor interest in uranium and energy-related companies in 2025. These were:
- US Federal executive orders
- Tech giants continued commitment to nuclear power
- Small Modular Reactor (SMR) projects at military outposts
- Continued AI capex growth
With so much focus on this sector, it's little wonder they have been doing well.
We recently launched the VanEck Uranium and Energy Innovation ETF (URAN) which has exposure to 25 global companies with exposure to uranium and nuclear energy infrastructure sectors. What is unique about URAN is that, unlike other similar ETFs, its constituents must generate at least 50% (25% for current constituents) of their revenues or expected revenues from uranium mining or uranium mining projects under development, and/or at least 50% (greater than 0% for current constituents) of their revenues from nuclear energy infrastructure (this may include companies whose business activity involves: projects related to the development and commercialisation of nuclear fusion technology; molten salt nuclear reactor research; construction, engineering, and maintenance of nuclear power facilities and nuclear reactors; equipment, technology, or services to the nuclear power industry).
As a result of this design, URAN provides a broader and more balanced exposure across the nuclear energy value chain than other uranium-focused ETFs trading on ASX.
URAN’s index also incorporates exclusionary screens, which are subject to gross revenue thresholds, by removing companies with verified involvement in controversial weapons (e.g. depleted uranium and nuclear weapons outside the Non-Proliferation Treaty), civilian firearms activities, as well as gambling, oil sands, thermal coal mining and tobacco. We believe a suitable investment should consider companies that meet certain minimum safeguards. These exclusions ensure that URAN’s holdings align with minimum safeguards and humanitarian standards, supported by norms-based screening consistent with international human rights principles.
Below are three companies in URAN that are not in similar ASX ETFs:
Hitachi, Ltd. (4.76% of portfolio, year-to-date return 31.88%)
Japanese multinational Hitachi is a holding in URAN due to its Green Energy & Mobility business segment, which supports the nuclear industry.
Hitachi has been involved in the nuclear power industry since the 1950s and has been active in constructing and maintaining boiling water reactors (BWRs) since the 1970s. Its joint venture with GE, to form GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy, is developing SMRs, such as the BWRX-300.
Fuji Electric Co., Ltd. (4.19% of portfolio, year-to-date return 27.47%)
Also in Japan, Fuji Electric is included in URAN due to its exposure to the nuclear industry that primarily comes via its Power and Social Infrastructure division, which is a world-leading manufacturer of nuclear power-related equipment.
AtkinsRéalis Group Inc (3.91% of portfolio, year-to-date return 26.00%)
Canadian engineering company AtkinsRéalis Group’s power sector provides services in the environment and water, the transmission and distribution of energy, including Nuclear. Its nuclear business focuses on supporting clients across the life cycle with procurement and construction management, field, technology services, spare parts, reactor support and decommissioning, and waste management.
Portfolio weights and return data source: FactSet, as at 31 October 2025.
This is URAN’s current top 10. You can see that Hitachi is in the top 10 (Fuji Electric was the 12thlargest holding at the end of last month)
Table 1: URAN’s Top 10 holdings
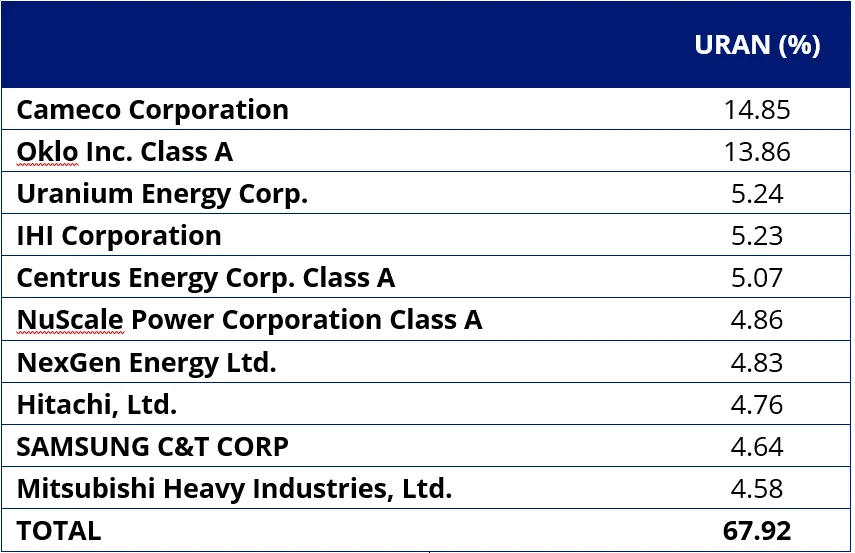
Source: FactSet, as at 31 October 2025.
Another difference is that URAN provides, provides a broad and balanced exposure across the uranium and nuclear energy value chain. Other peers, by contrast, may be overly concentrated (i.e. have an exposure greater than 50%, or 90% in one instance!) in the ‘coal & consumable fuels’ GICS sub-industry sector (i.e. uranium mining and production) with no exposure to companies involved in nuclear energy infrastructure or advanced nuclear technologies.
Chart 2: URAN’s sub-industry sector breakdown
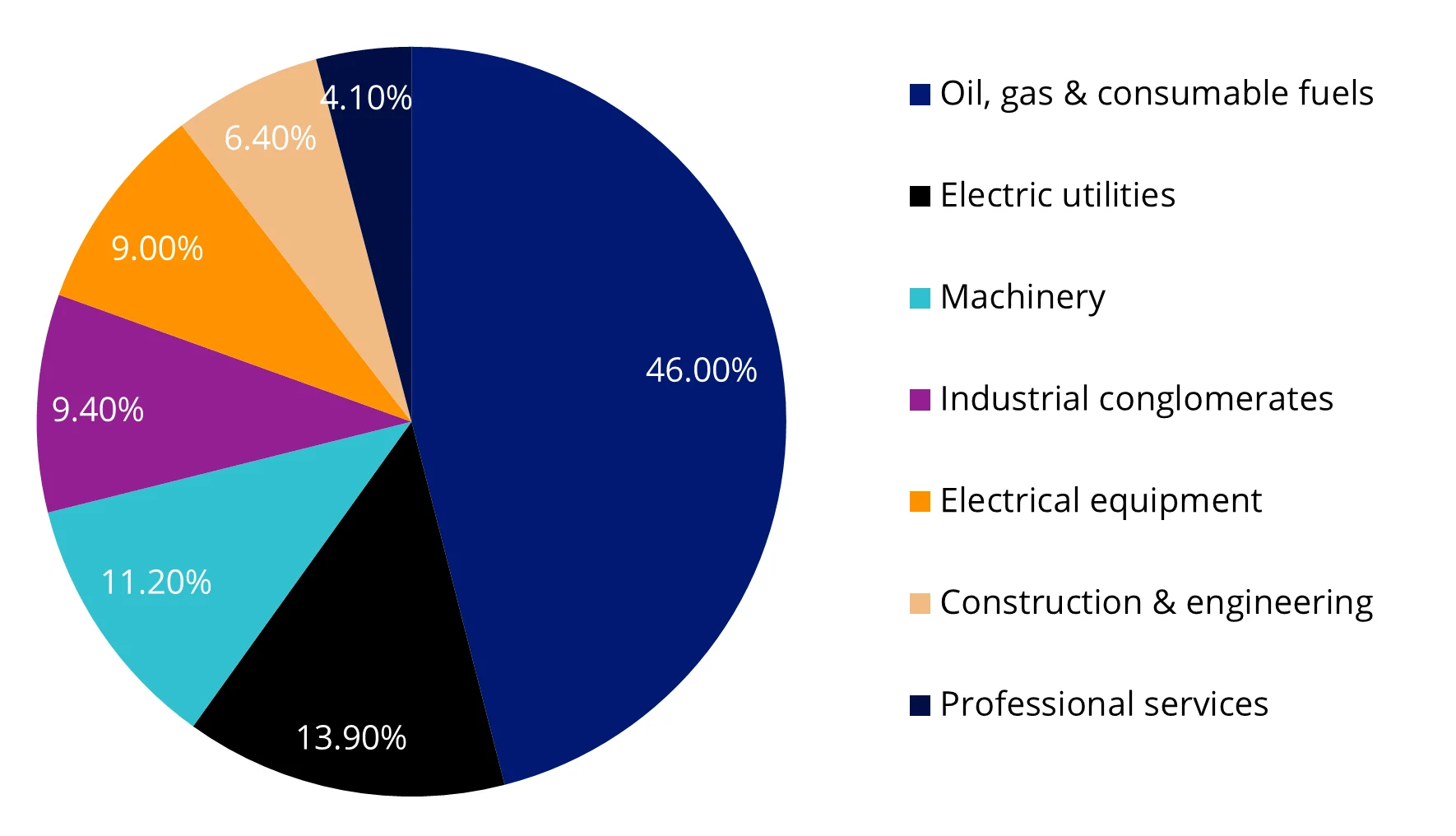
Source: FactSet, as at 31 October 2025.
What to consider when investing in nuclear energy companies
As the world shifts toward clean energy and decarbonisation, nuclear energy companies are becoming an area of the energy market that investors are considering. However, nuclear power comes with unique risks and factors that investors should weigh carefully.
Regulatory risks in the space are notable, as nuclear power is one of the most heavily regulated industries. Regulatory changes or heightened safety requirements can impact companies in numerous ways, making it essential to stay informed about the regulatory landscape. Geopolitical factors also play a role, especially in uranium mining, where operations in politically unstable regions can disrupt supply and influence pricing.
On the positive side, global government support for nuclear power is increasing as many countries seek to meet decarbonisation targets. Many governments offer incentives for advanced nuclear technologies, particularly SMRs, which could spur growth across the sector. Additionally, rising demand for clean, reliable energy, driven by sectors such as data centres and AI, underscores nuclear energy’s role as a stable, round-the-clock energy source.
Finally, nuclear is a long-term investment, with new power facilities and technology often requiring years to construct and bring online. A diversified and global approach, with exposure to nuclear energy infrastructure or advanced nuclear technologies, can help mitigate the risks tied to the nuclear industry, allowing investors to benefit from the sector’s robust potential while managing volatility for a more balanced return over the long term.
Invest in the top energy innovators powering the future
There is no doubt about the current appeal of Uranium and energy ETFs. URAN is a portfolio of the largest global companies involved in the uranium mining and nuclear energy sectors, which are typically under-represented in benchmarks. The sector is well-positioned, we think, to meet the accelerating demand for electricity from the rapid expansion of AI, computational power and digital infrastructure.
Not all Uranium ETFs are the same.
For further information, you can contact us via [email protected]
Key risks: An investment in the ETF carries risks associated with: ASX trading time differences, financial markets generally, individual company management, industry sectors, country or sector concentration, political, regulatory and tax risks, fund operations, liquidity and tracking an index. See the PDS for more details on risk.
Published: 14 November 2025
Any views expressed are opinions of the author at the time of writing and is not a recommendation to act.
VanEck Investments Limited (ACN 146 596 116 AFSL 416755) (VanEck) is the issuer and responsible entity of all VanEck exchange traded funds (Funds) trading on the ASX. This information is general in nature and not personal advice, it does not take into account any person’s financial objectives, situation or needs. The product disclosure statement (PDS) and the target market determination (TMD) for all Funds are available at vaneck.com.au. You should consider whether or not any Fund is appropriate for you. Investments in a Fund involve risks associated with financial markets. These risks vary depending on a Fund’s investment objective. Refer to the applicable PDS and TMD for more details on risks. Investment returns and capital are not guaranteed.
MarketVector Indexes (MarketVector), is a related body corporate of VanEck Investments Limited, the responsible entity and issuer of URAN.